What is 5G?
Summary: 5G is the latest type of mobile network, and the coverage is expanding. Learn what makes 5G different than 4G LTE, how fast 5G really is, and how you’ll benefit from a faster mobile phone connection.
If you’re tuned into the tech world — or have recently considered upgrading your cell phone — you’ve probably heard of 5G. But what is it?
Simply put, 5G is the latest evolution of wireless technology, and it’s going to bring faster downloads and lower lag times. 5G phones initially used 4G networks, and even as 5G moves to be a “standalone,” it will still require assistance from 4G. This will all be done seamlessly, giving you the best coverage wherever you are.
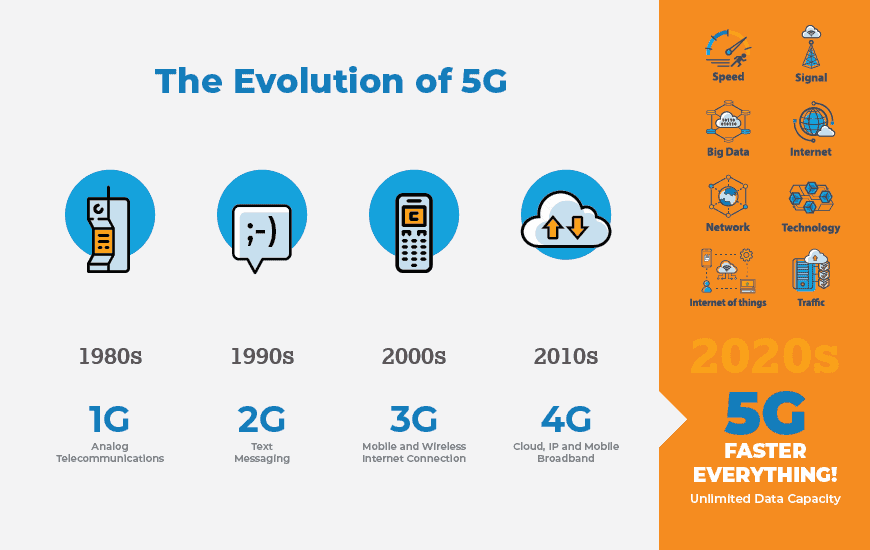
When 4G was released in the 2010s, it revolutionized how we use cell phones. Now, 5G is also expected to make our mobile lives better and more efficient.
The rollout is still in the early phases, but the progress is promising so far. While 5G is already available in most cities, coverage is rapidly expanding to less densely-populated areas. Even if 5G isn’t yet available near you, we’re breaking down everything you need to know.
What Makes 5G Different than 4G?
In some ways, 4G is the backbone of 5G. We couldn’t have gotten to this point without the advent of 4G, and it will be around for quite some time as 5G becomes fully enmeshed in our mobile world.
Simply put, 5G is the latest evolution of wireless technology, and it’s going to bring faster downloads and lower lag times.
It’s helpful to think back to the 4G evolution. While 4G phones were first created in 2010, the biggest changes from the 4G network and applications that required that technology came later (think apps like Uber and higher quality video calls, both of which appeared in 2013). According to PCMag, we can expect the biggest benefits of 5G to start showing up in 2022 and 2023.
How Does 5G Work?
There are three types of 5G — low-band, mid-band, and high-band. Each type serves a different purpose, and all three offer unique speeds:
Low-band: can more easily blanket large areas and travel farther. This is the slowest of the 5G options, but it’s still noticeably faster than 4G.
Mid-band: this is the ideal spot between speed and coverage. A limited number of cell phone carriers are currently equipped for mid-band 5G.
High-band: this frequency offers the fastest speeds from 5G, but is easily obstructed by trees and buildings, making it only suitable for covering a small area. This is also called millimeter wave (mmWave) 5G.
How Fast is 5G?
The speed you experience will depend on the frequency you’re connected to, but even low-band 5G will be faster than 4G LTE. In areas where high-band 5G is available, the networks are expected to be at least 10 times faster than 4G — and some experts say it could eventually be 100 times faster.
Let’s put that in perspective. According to PCMag, the increase in speed will save the average consumer 24 hours in download time. Movie download times will go from seven minutes to six seconds and large game downloads will be nearly seven hours faster.
While this is promising, your actual speed will still depend on things like location and network traffic. As 5G becomes widely available, that coverage should be more stable — even when compared to the current networks.
Why Do We Need 5G?
You might feel like your mobile phone works just fine as it is — why worry about creating a whole new network? There are a few reasons for 5G, and a ton of ways it’s expected to improve our lives.
Movie download times will go from seven minutes to six seconds and large game downloads will be nearly seven hours faster.
Perhaps most importantly, the existing 4G networks are getting congested, leading to a reduction in speed, especially during the middle of the day. Your cell phone functions on radio waves, and as we continue to consume more data every year, there are breakdowns in service. 5G is better equipped to handle thousands of devices at a time without service gaps.
As entire cities use more smart devices (including self-driving cars), 5G will be able to handle the increase in demand. The technology opens up a ton of options, from virtually-enhanced events to be able to send messages at a crowded concert to autonomous cars reading maps and traffic patterns – and responding – in real time.
The expansion of 5G also advances the possibilities of smart homes, virtual reality, and even remote surgeries. The capabilities of 5G networks hold a lot of promise for what is coming in the future. Just as we couldn’t have imagined the real-time tracking of ride services like Uber in 2009 when 4G was first being built, it’s difficult to say just what 5G holds in store — but it’s safe to say we’re looking forward to it.
Even if 5G isn’t available in your neighborhood yet, you can rest assured that it will bring a better connection when it arrives. Between the time you’ll save downloading content, the new opportunities for enhanced events, and a stronger connection to what we already love, the future of mobile is looking bright.